Offline-First Android System Design: A Complete Guide - 2
A comprehensive deep-dive into building Android applications that work seamlessly offline, covering architecture patterns, synchronization strategies, edge cases, and real-world implementation approaches.
Table of Contents
Part - 1
Introduction to Offline-First
Core Architecture Patterns
Data Synchronization Strategies
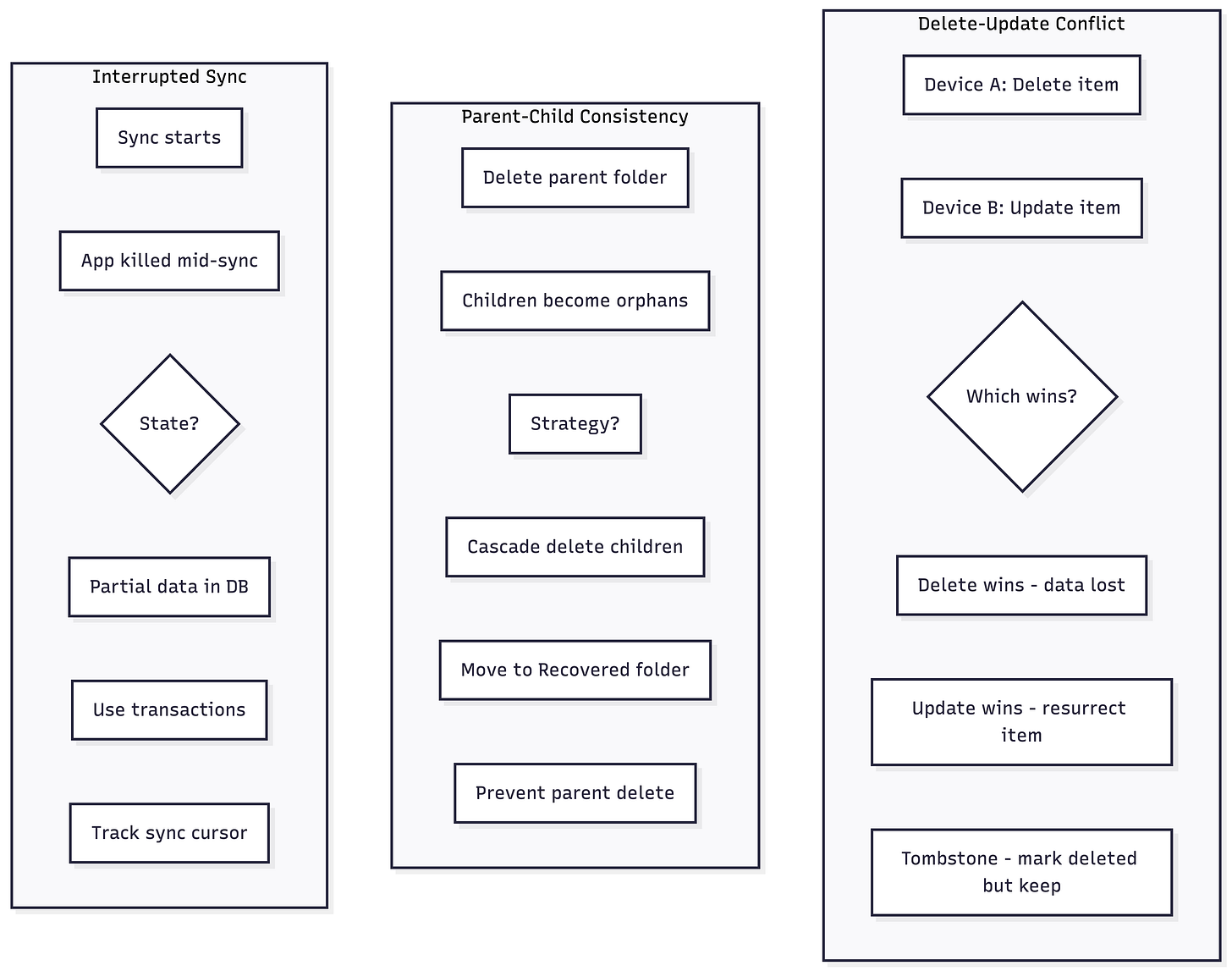
Conflict Resolution
Part - 2
Caching Architecture
Network State Management
Background Sync & WorkManager
Edge Cases & Error Handling
Testing Offline Scenarios
Best Practices & Patterns
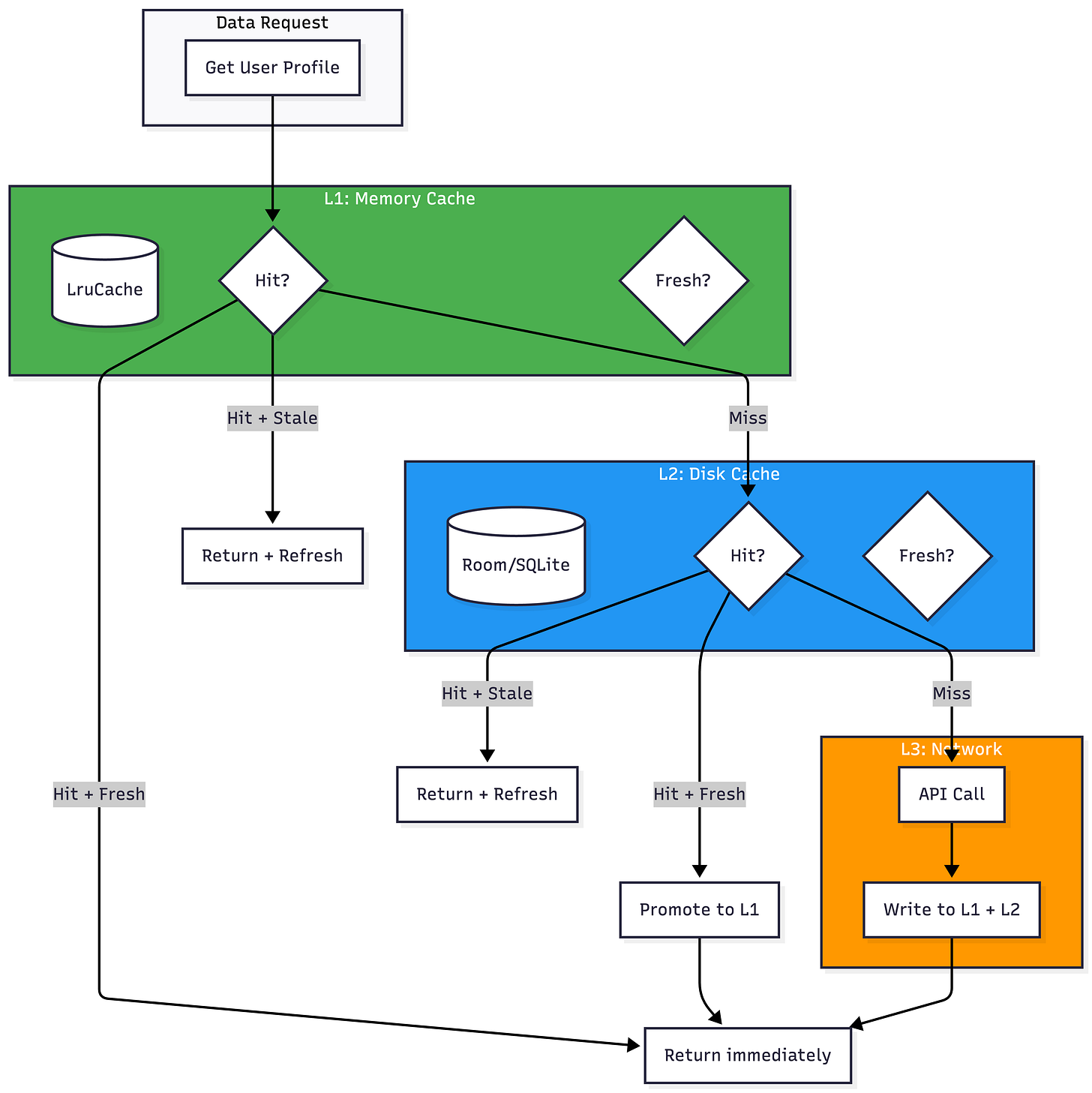
Caching Architecture
Multi-Layer Cache Design
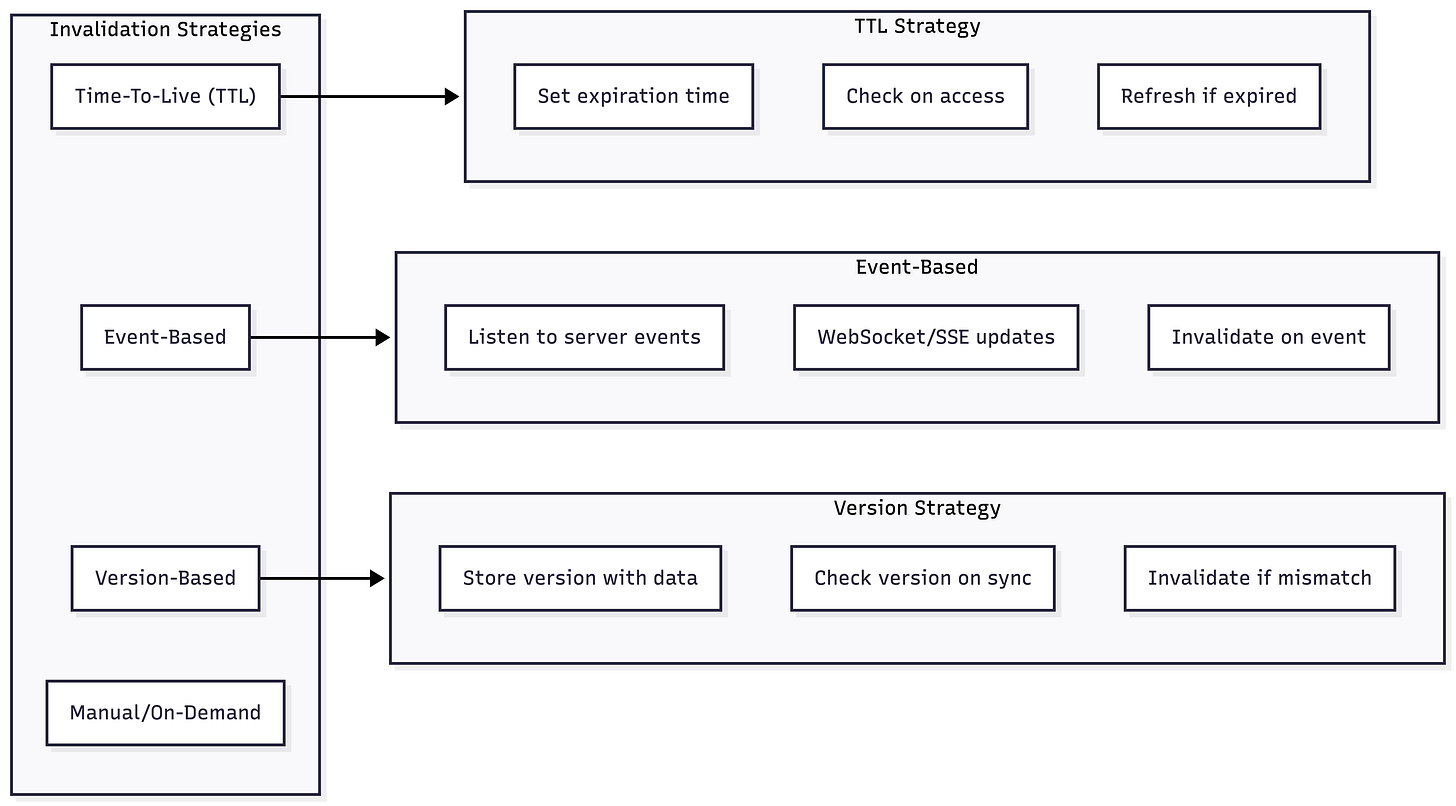
Cache Invalidation Strategies
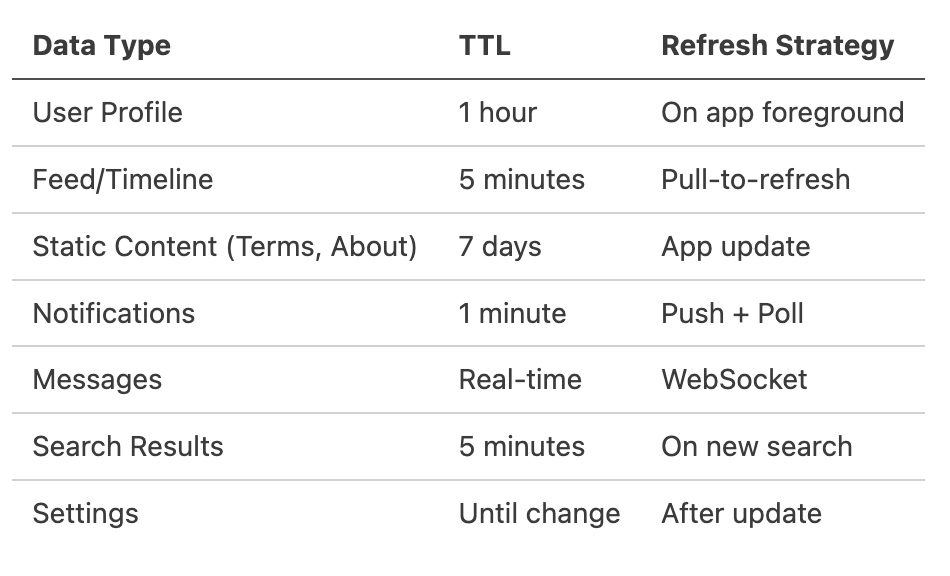
Cache Freshness Policies
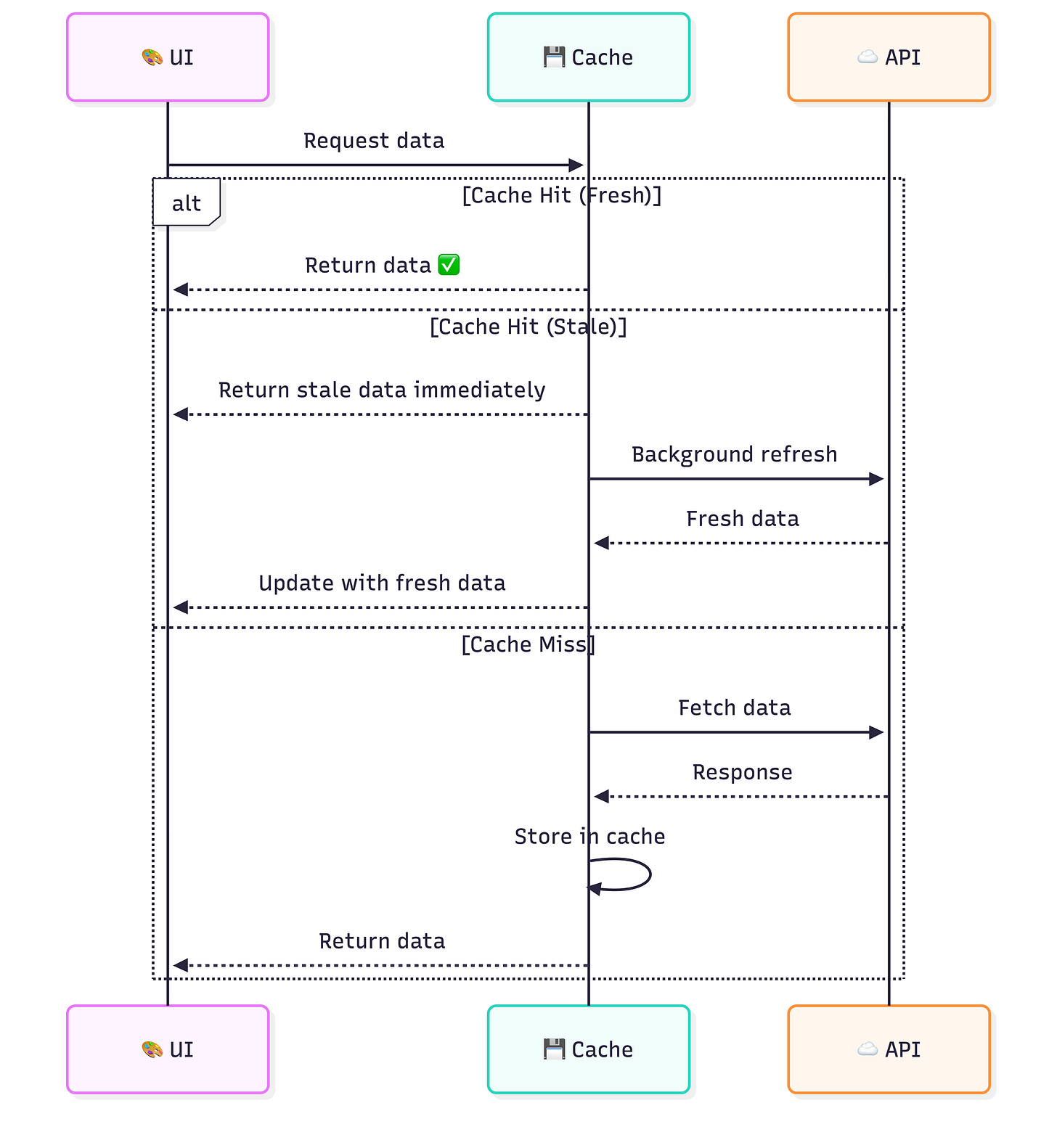
Stale-While-Revalidate Pattern
// Cache-Control inspired freshness check
data class CachedData<T>(
val data: T,
val cachedAt: Long,
val maxAge: Long, // Fresh for this duration
val staleWhileRevalidate: Long // Can serve stale for this additional duration
) {
val isFresh: Boolean
get() = System.currentTimeMillis() - cachedAt < maxAge
val isStaleButUsable: Boolean
get() {
val age = System.currentTimeMillis() - cachedAt
return age >= maxAge && age < (maxAge + staleWhileRevalidate)
}
val isExpired: Boolean
get() = System.currentTimeMillis() - cachedAt >= (maxAge + staleWhileRevalidate)
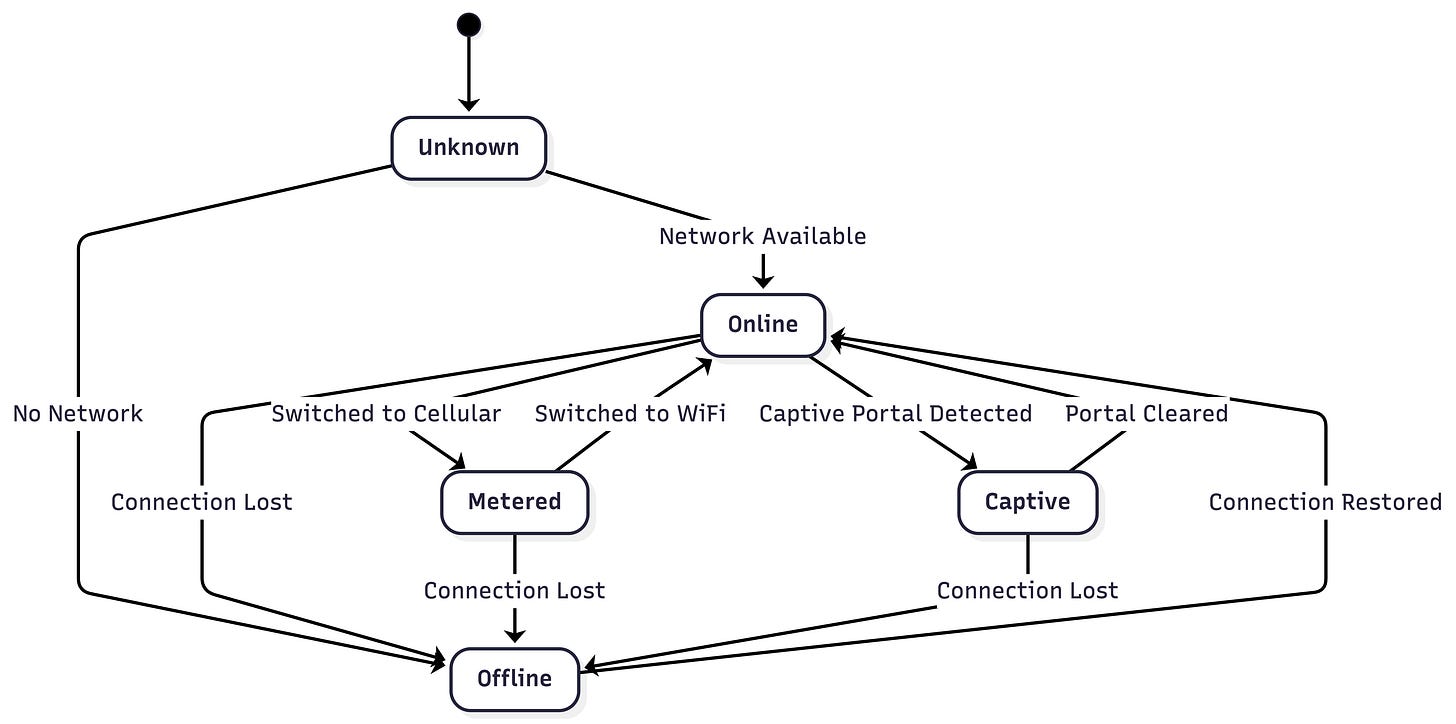
}Network State Management
Connectivity Observation
Network State Types
sealed class NetworkState {
object Unknown : NetworkState()
data class Online(
val type: ConnectionType,
val isMetered: Boolean,
val downstreamBandwidthKbps: Int
) : NetworkState()
object Offline : NetworkState()
data class CaptivePortal(
val portalUrl: String?
) : NetworkState()
}
enum class ConnectionType {
WIFI, CELLULAR_5G, CELLULAR_4G, CELLULAR_3G, CELLULAR_2G, ETHERNET, UNKNOWN
}
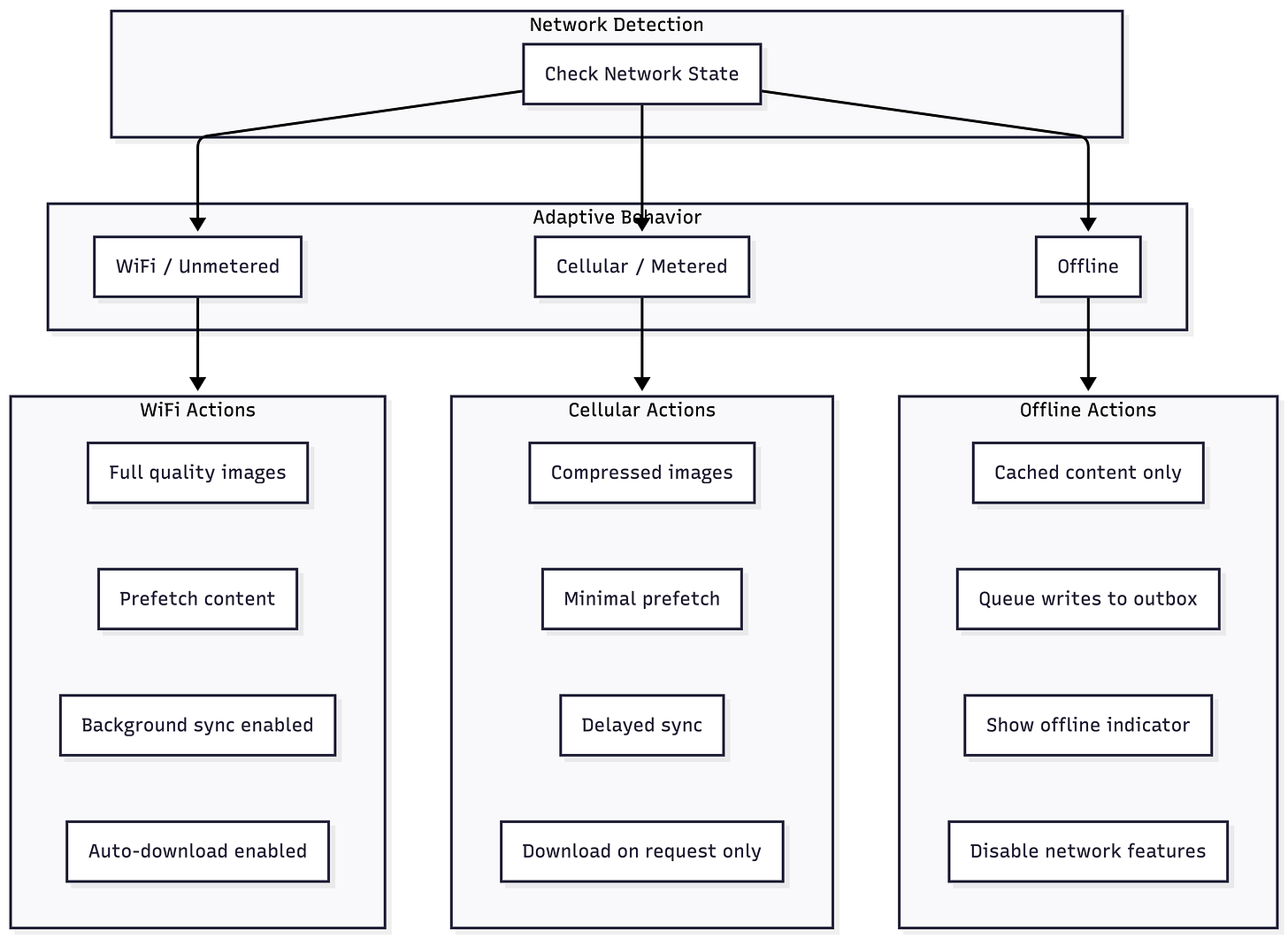
Adaptive Behavior Based on Network
Connectivity Monitoring Implementation
// Observing network state changes
class NetworkMonitor @Inject constructor(
@ApplicationContext private val context: Context
) {
private val connectivityManager =
context.getSystemService<ConnectivityManager>()
val networkState: Flow<NetworkState> = callbackFlow {
val callback = object : ConnectivityManager.NetworkCallback() {
override fun onAvailable(network: Network) {
trySend(determineNetworkState())
}
override fun onLost(network: Network) {
trySend(NetworkState.Offline)
}
override fun onCapabilitiesChanged(
network: Network,
capabilities: NetworkCapabilities
) {
trySend(determineNetworkState(capabilities))
}
}
val request = NetworkRequest.Builder()
.addCapability(NetworkCapabilities.NET_CAPABILITY_INTERNET)
.build()
connectivityManager?.registerNetworkCallback(request, callback)
// Emit initial state
trySend(determineNetworkState())
awaitClose {
connectivityManager?.unregisterNetworkCallback(callback)
}
}.distinctUntilChanged()
private fun determineNetworkState(
capabilities: NetworkCapabilities? = null
): NetworkState {
val caps = capabilities
?: connectivityManager?.activeNetwork?.let {
connectivityManager.getNetworkCapabilities(it)
}
?: return NetworkState.Offline
// Check for captive portal
if (!caps.hasCapability(NetworkCapabilities.NET_CAPABILITY_VALIDATED)) {
return NetworkState.CaptivePortal(null)
}
return NetworkState.Online(
type = determineConnectionType(caps),
isMetered = !caps.hasCapability(
NetworkCapabilities.NET_CAPABILITY_NOT_METERED
),
downstreamBandwidthKbps = caps.linkDownstreamBandwidthKbps
)
}
}Background Sync & WorkManager
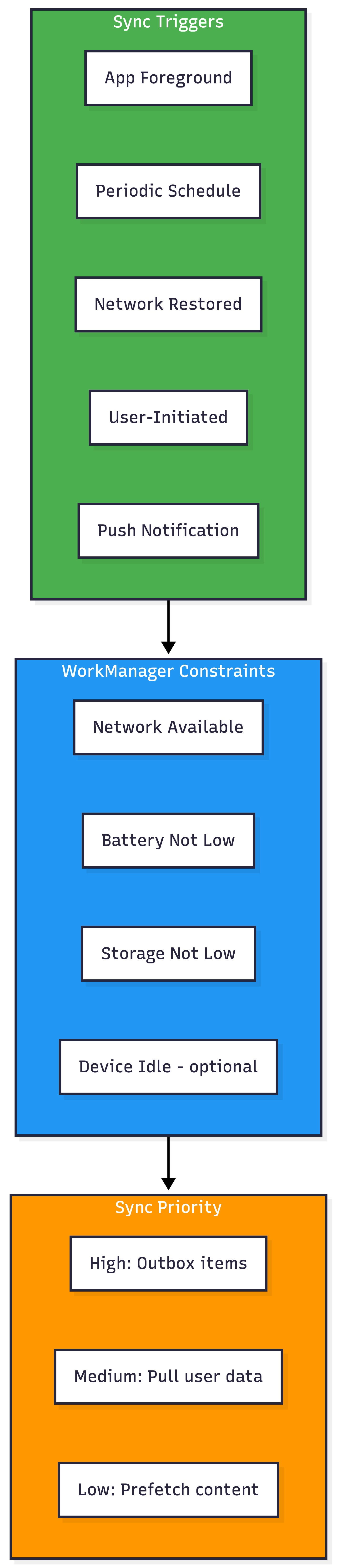
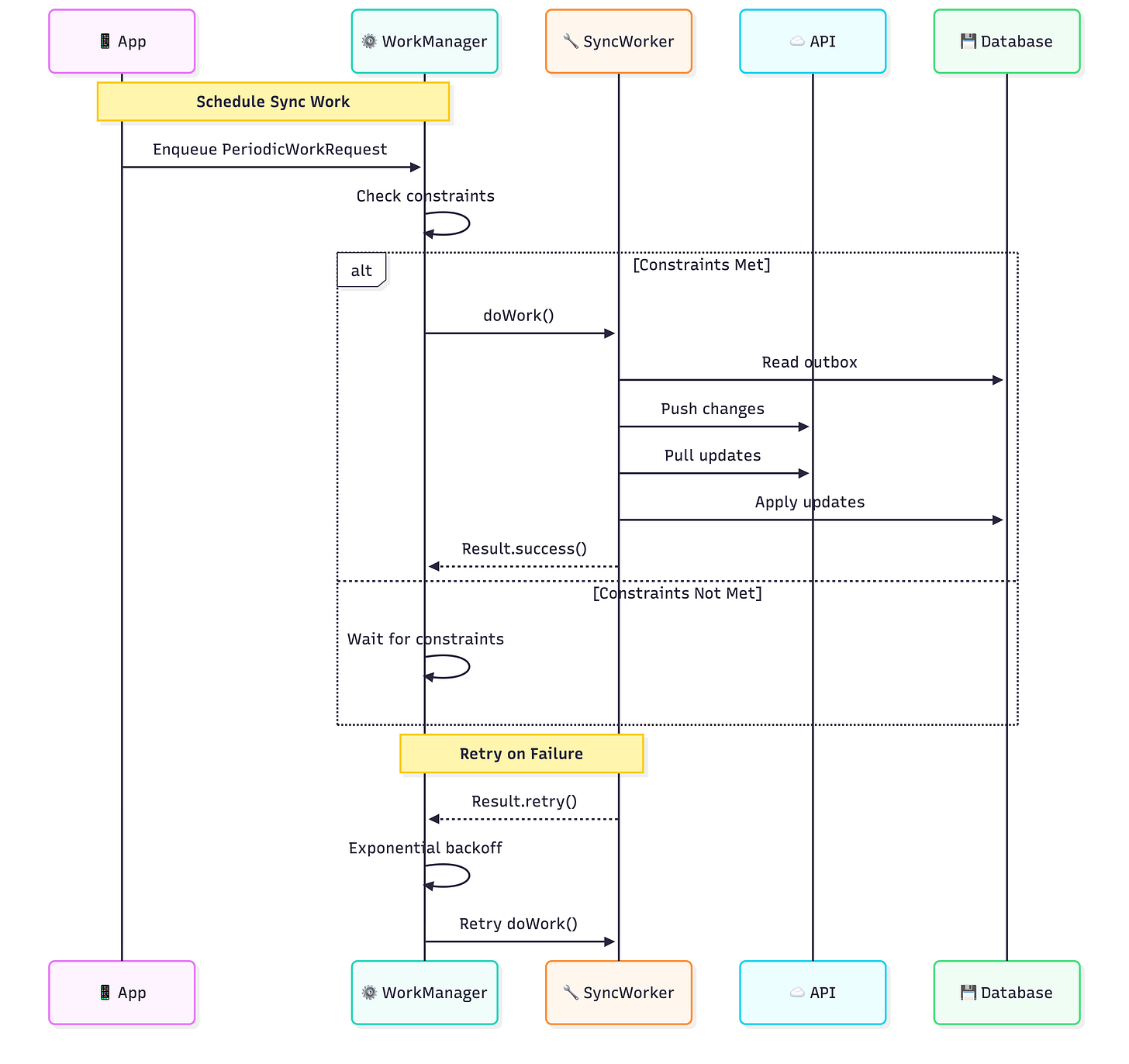
Sync Scheduling Strategy
WorkManager Configuration
Sync Worker Implementation
@HiltWorker
class SyncWorker @AssistedInject constructor(
@Assisted context: Context,
@Assisted params: WorkerParameters,
private val syncEngine: SyncEngine,
private val notificationHelper: SyncNotificationHelper
) : CoroutineWorker(context, params) {
override suspend fun doWork(): Result {
// Show progress for long-running sync
setForeground(createForegroundInfo())
return try {
val syncResult = syncEngine.performFullSync()
when {
syncResult.isSuccess -> {
notificationHelper.showSyncComplete(syncResult.itemsSynced)
Result.success()
}
syncResult.hasConflicts -> {
notificationHelper.showConflictsNeedResolution(
syncResult.conflicts.size
)
Result.success() // Still success, conflicts are queued
}
syncResult.isPartialFailure -> {
// Some items synced, retry for the rest
if (runAttemptCount < 3) Result.retry()
else Result.success() // Give up on remaining items
}
else -> {
if (runAttemptCount < 5) Result.retry()
else Result.failure()
}
}
} catch (e: Exception) {
if (runAttemptCount < 3) Result.retry()
else Result.failure(workDataOf("error" to e.message))
}
}
private fun createForegroundInfo(): ForegroundInfo {
return ForegroundInfo(
SYNC_NOTIFICATION_ID,
notificationHelper.createSyncInProgressNotification()
)
}
}
// Scheduling the sync worker
object SyncScheduler {
fun schedulePeriodicSync(workManager: WorkManager) {
val constraints = Constraints.Builder()
.setRequiredNetworkType(NetworkType.CONNECTED)
.setRequiresBatteryNotLow(true)
.build()
val syncRequest = PeriodicWorkRequestBuilder<SyncWorker>(
repeatInterval = 15,
repeatIntervalTimeUnit = TimeUnit.MINUTES,
flexTimeInterval = 5,
flexTimeIntervalUnit = TimeUnit.MINUTES
)
.setConstraints(constraints)
.setBackoffCriteria(
BackoffPolicy.EXPONENTIAL,
WorkRequest.MIN_BACKOFF_MILLIS,
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS
)
.build()
workManager.enqueueUniquePeriodicWork(
"periodic_sync",
ExistingPeriodicWorkPolicy.KEEP,
syncRequest
)
}
fun scheduleImmediateSync(workManager: WorkManager) {
val syncRequest = OneTimeWorkRequestBuilder<SyncWorker>()
.setConstraints(
Constraints.Builder()
.setRequiredNetworkType(NetworkType.CONNECTED)
.build()
)
.setExpedited(OutOfQuotaPolicy.RUN_AS_NON_EXPEDITED_WORK_REQUEST)
.build()
workManager.enqueueUniqueWork(
"immediate_sync",
ExistingWorkPolicy.REPLACE,
syncRequest
)
}
}Edge Cases & Error Handling
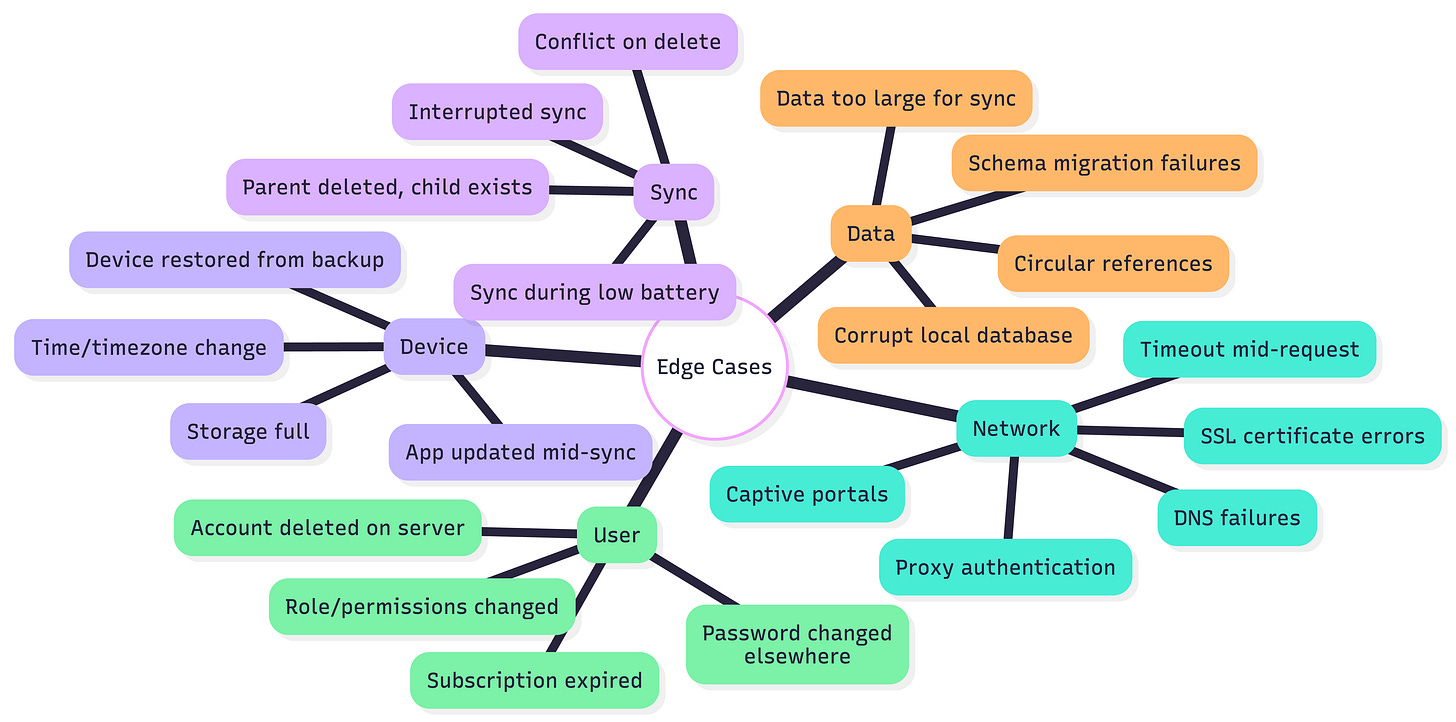
Complete Edge Case Catalog
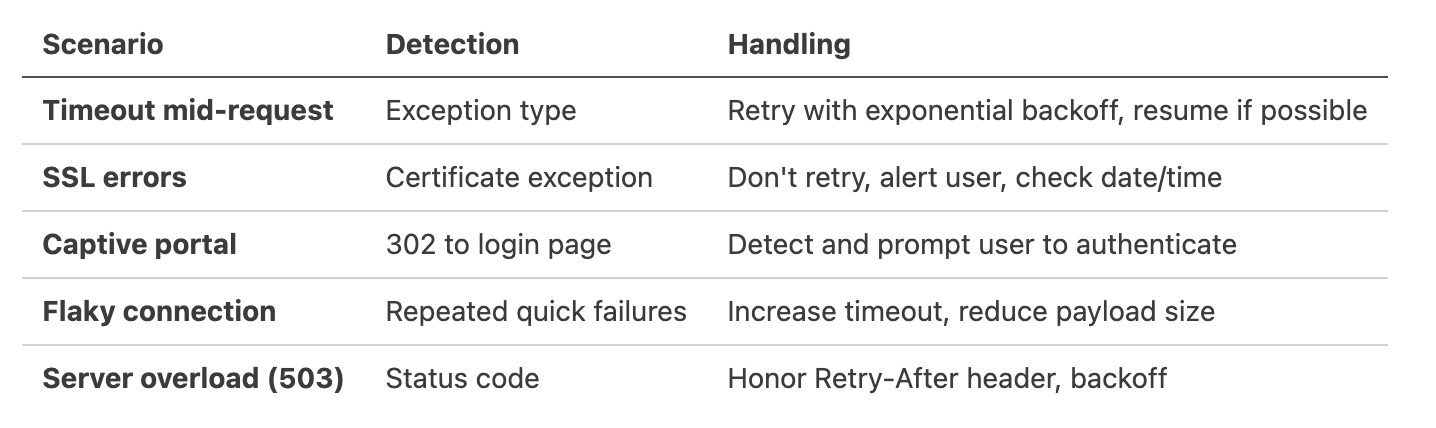
Network Edge Cases
Data Consistency Edge Cases
Storage Edge Cases
// Handling storage pressure
class StorageManager @Inject constructor(
@ApplicationContext private val context: Context
) {
fun getAvailableSpace(): Long {
val stat = StatFs(context.filesDir.path)
return stat.availableBytes
}
fun isStorageLow(): Boolean {
val available = getAvailableSpace()
val threshold = 100 * 1024 * 1024 // 100MB
return available < threshold
}
suspend fun freeUpSpace(targetBytes: Long): Boolean {
var freedBytes = 0L
// Priority order for deletion
val deletionCandidates = listOf(
{ clearImageCache() },
{ clearOldSyncLogs() },
{ clearExpiredCacheData() },
{ compactDatabase() },
// Never auto-delete user content
)
for (action in deletionCandidates) {
if (freedBytes >= targetBytes) break
freedBytes += action()
}
return freedBytes >= targetBytes
}
}
// Graceful handling when storage is full
suspend fun saveWithStorageCheck(data: Data): Result<Unit> {
return try {
if (storageManager.isStorageLow()) {
val needed = estimateSize(data)
val freed = storageManager.freeUpSpace(needed)
if (!freed) {
return Result.failure(InsufficientStorageException())
}
}
database.save(data)
Result.success(Unit)
} catch (e: SQLiteFullException) {
Result.failure(InsufficientStorageException(e))
}
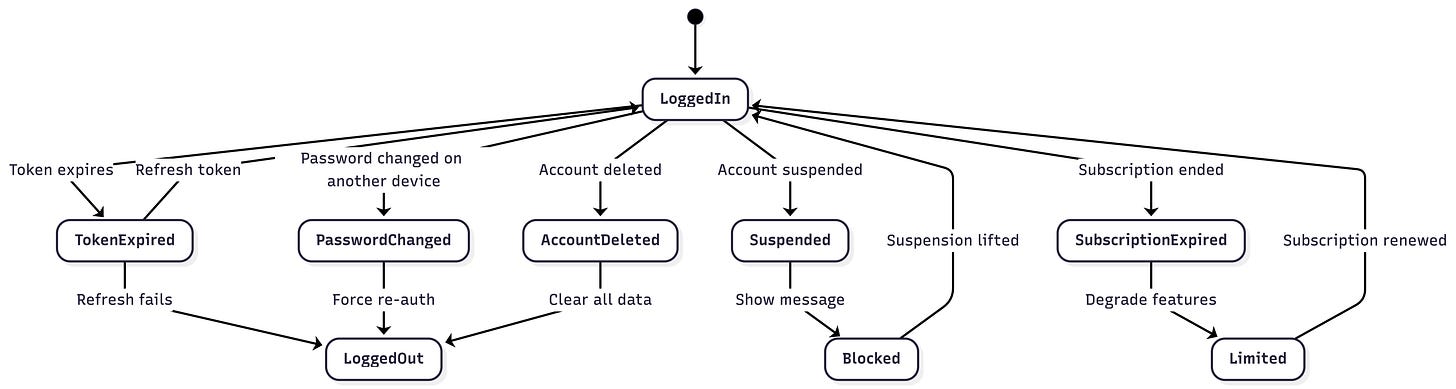
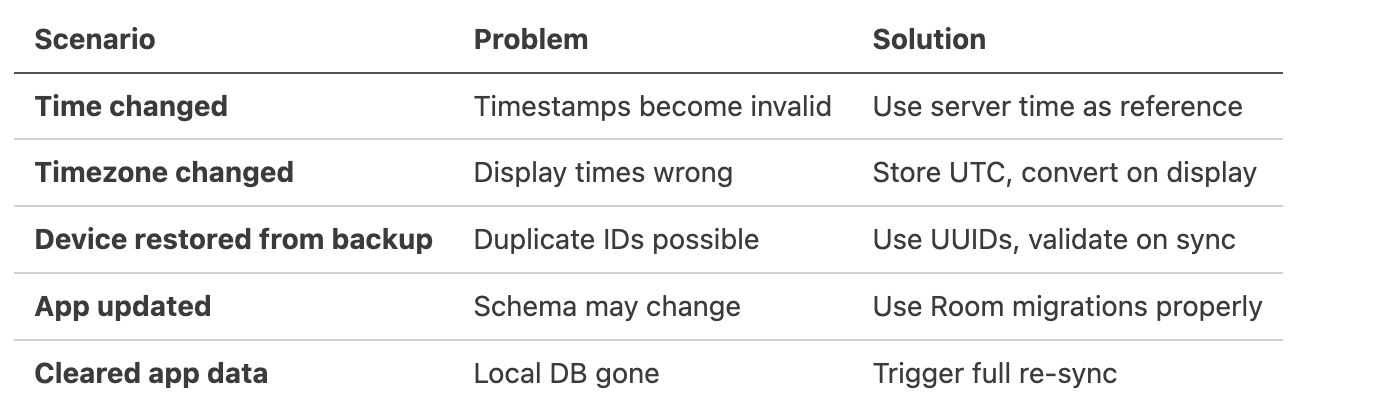
}Account State Edge Cases
Device State Edge Cases
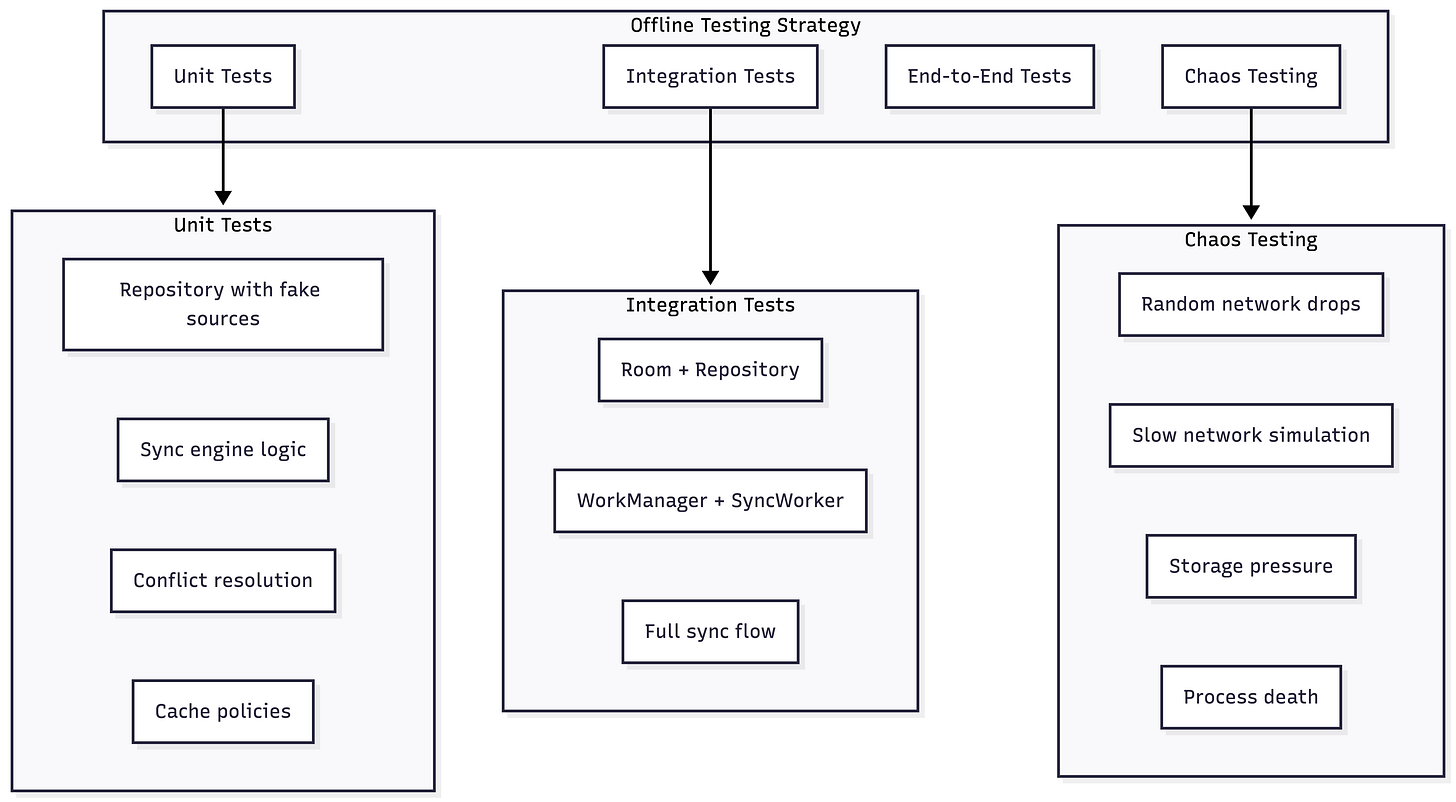
Testing Offline Scenarios
Test Categories
Test Scenarios Checklist
## Network Conditions
- [ ] Complete offline mode
- [ ] Transition from online to offline during operation
- [ ] Transition from offline to online
- [ ] Slow network (simulate 2G/3G)
- [ ] High latency network
- [ ] Intermittent connectivity (flaky)
- [ ] WiFi to cellular transition
- [ ] Airplane mode toggle
## Data Operations
- [ ] Create while offline
- [ ] Update while offline
- [ ] Delete while offline
- [ ] Conflict: same item modified on two devices
- [ ] Conflict: item deleted on one, modified on other
- [ ] Large batch operations offline
- [ ] Sync with thousands of items
## Edge Cases
- [ ] Storage nearly full
- [ ] Process killed during sync
- [ ] App update during offline period
- [ ] Account state changes while offline
- [ ] Clock skew between devices
- [ ] Corrupt cache recovery
Simulating Network Conditions
// Fake network data source for testing
class FakeNetworkDataSource : NetworkDataSource {
var shouldFail = false
var latencyMs = 0L
var failureRate = 0.0 // 0.0 to 1.0
private val random = Random()
override suspend fun fetch(): Result<Data> {
delay(latencyMs)
if (shouldFail || random.nextDouble() < failureRate) {
return Result.failure(IOException("Simulated network failure"))
}
return Result.success(testData)
}
}
// Using ADB to test on device
// Simulate offline:
// adb shell svc wifi disable
// adb shell svc data disable
// Simulate slow network:
// adb shell tc qdisc add dev wlan0 root netem delay 500ms
// Simulate packet loss:
// adb shell tc qdisc add dev wlan0 root netem loss 20%Best Practices & Patterns
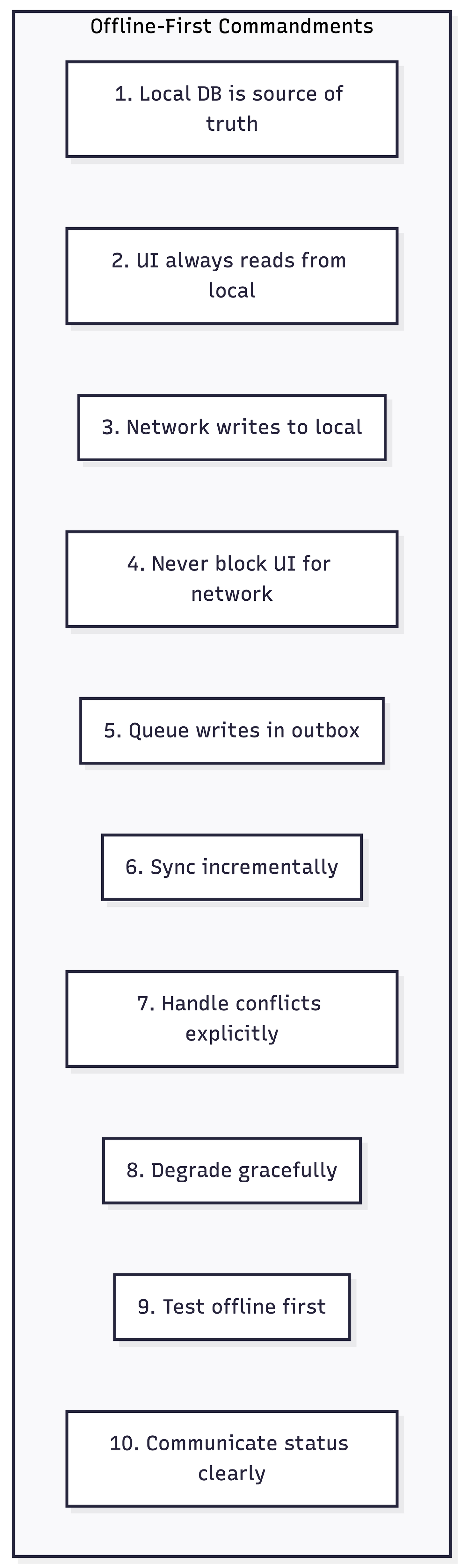
The Ten Commandments of Offline-First
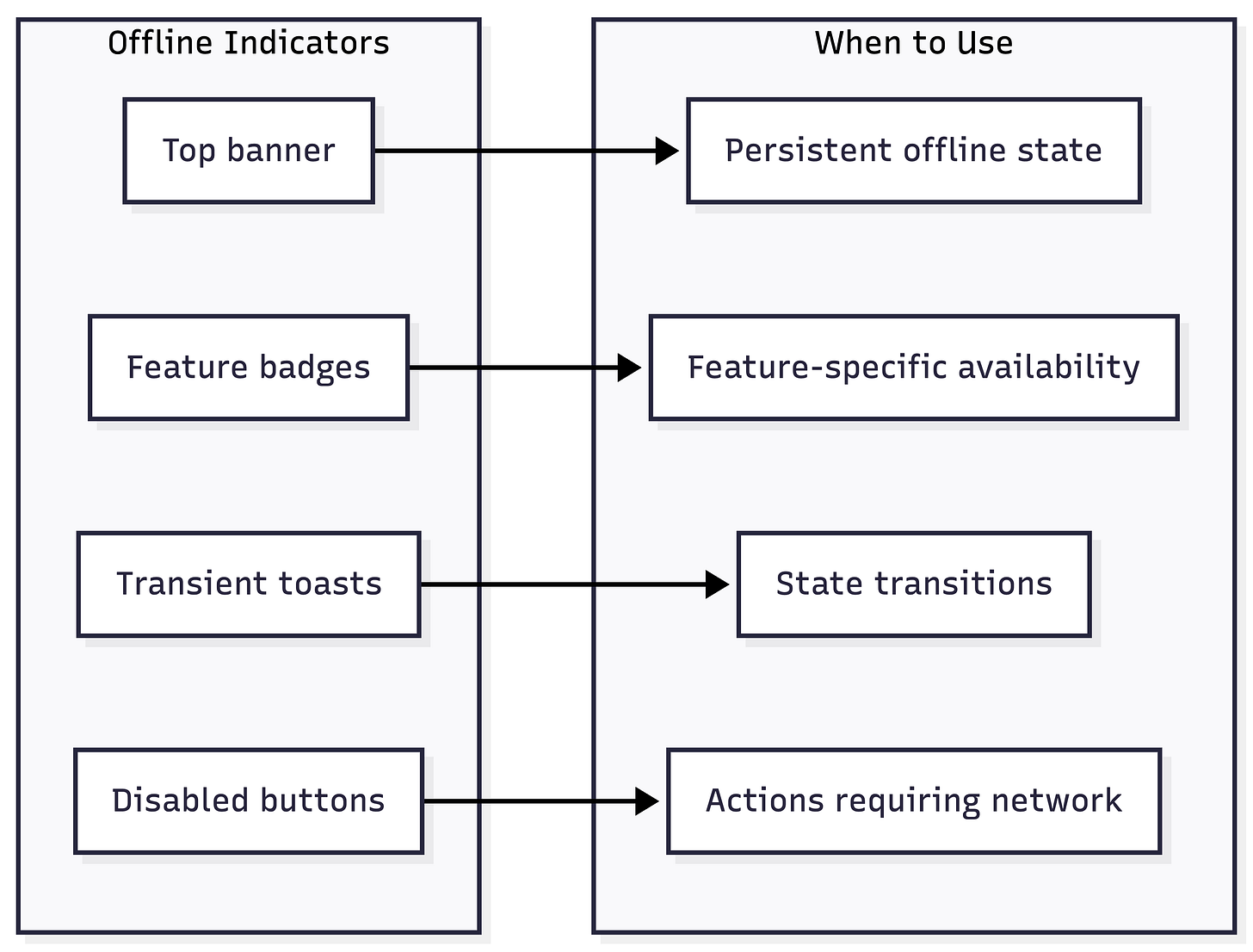
UI Patterns for Offline State
Best Practices for Offline UI:
Show offline status prominently but not intrusively
Indicate which content is cached vs. potentially stale
Disable (don’t hide) features requiring network
Show pending sync count when relevant
Celebrate successful sync completion subtly
Explain why certain features are unavailable
Data Model Patterns
// Every syncable entity should have these fields
interface Syncable {
val id: String // Client-generated UUID
val serverId: String? // Server-assigned ID (null until synced)
val version: Long // For conflict detection
val createdAt: Long // Local creation timestamp
val modifiedAt: Long // Last modification timestamp
val syncedAt: Long? // Last successful sync
val syncStatus: SyncStatus // Current sync state
}
enum class SyncStatus {
SYNCED, // Matches server state
PENDING_CREATE, // Created locally, not yet synced
PENDING_UPDATE, // Modified locally, not yet synced
PENDING_DELETE, // Marked for deletion, not yet synced
CONFLICT // Has unresolved conflict
}
// Extension to check if entity needs sync
val Syncable.needsSync: Boolean
get() = syncStatus != SyncStatus.SYNCED
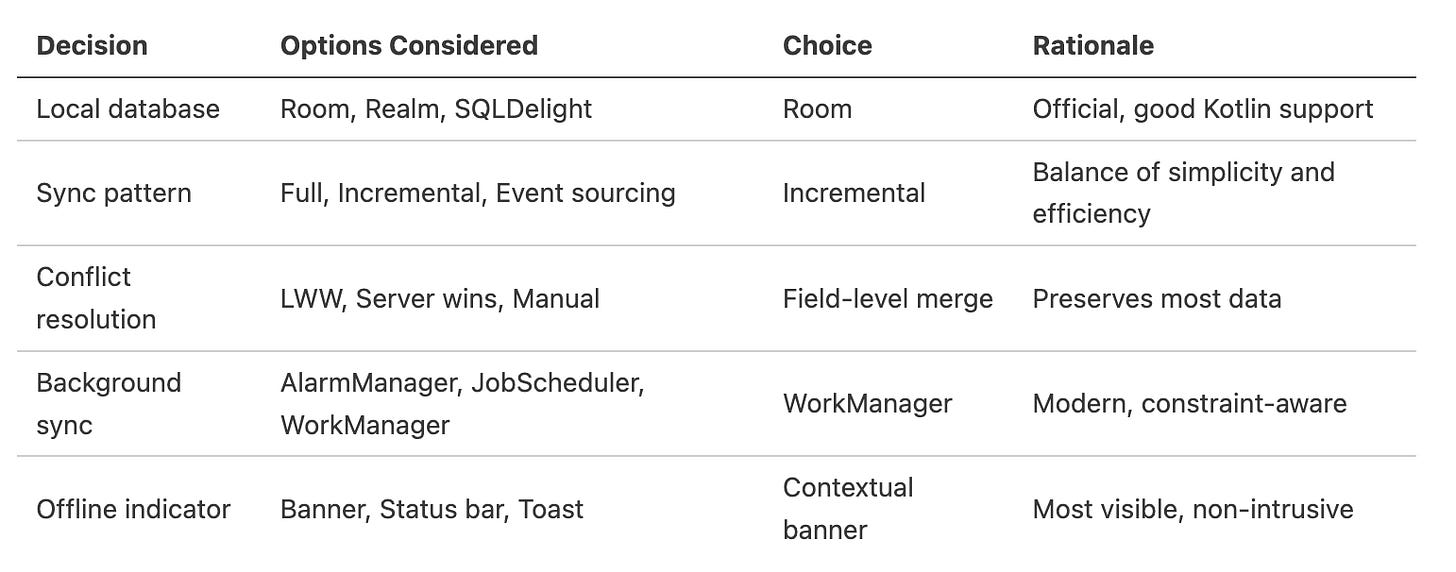
Architecture Decision Records
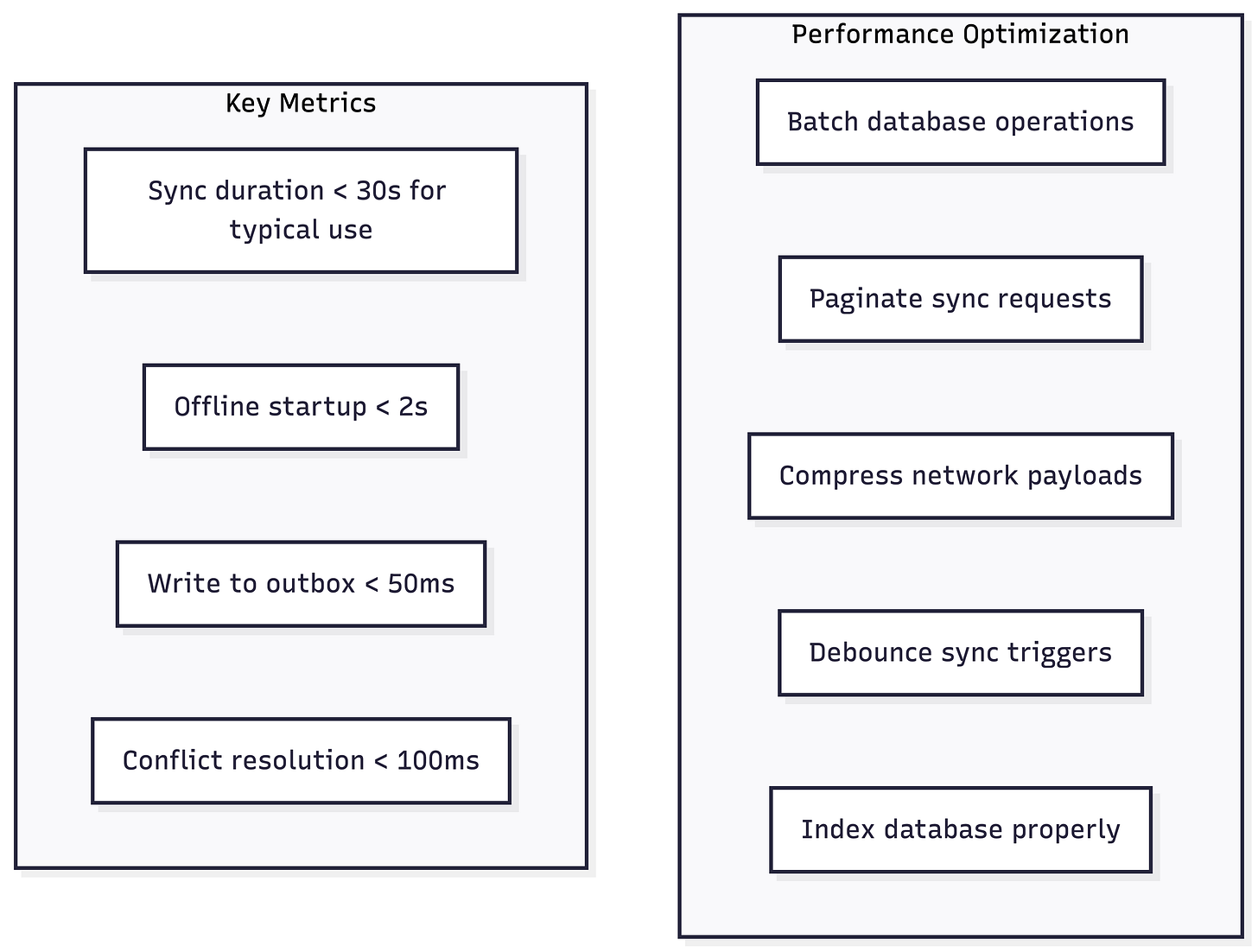
Performance Considerations
Conclusion
The Offline-First Architecture Checklist
## Foundation
- [ ] Room database as source of truth
- [ ] Repository pattern isolating data sources
- [ ] Outbox table for pending operations
- [ ] Sync status on all syncable entities
## Synchronization
- [ ] Incremental sync with tokens/cursors
- [ ] Bidirectional sync (push then pull)
- [ ] Conflict detection mechanism
- [ ] Conflict resolution strategy defined
## Error Handling
- [ ] Retry logic with exponential backoff
- [ ] Graceful degradation for all features
- [ ] Clear error communication to users
- [ ] Automatic recovery where possible
## Background Processing
- [ ] WorkManager for reliable sync
- [ ] Appropriate constraints set
- [ ] Battery and data usage considered
- [ ] Foreground service for long syncs
## User Experience
- [ ] Offline indicator visible
- [ ] Pending changes shown
- [ ] Stale data marked
- [ ] Sync status accessible
## Testing
- [ ] Offline scenarios tested
- [ ] Conflict resolution tested
- [ ] Slow/flaky network tested
- [ ] Edge cases coveredBuilding offline-first applications requires a fundamental shift in thinking. The network becomes an optimization, not a requirement. The result is applications that feel fast, reliable, and trustworthy—the hallmarks of great mobile software.
“The best network request is the one you never have to make.”



This is absoutely essential reading for anyone doing mobile dev. The section on simulating network states for tests is particulary brilliant - too many teams skip this and then get burned in production. I've seen apps crash spectacularly when users toggle airplane mode mid-sync. Your checklist aproach makes it actually managable to test those edge cases systematically.